模型训练
我们要解决的业务问题是预测广告请求出价成功的可能性,根据可能性决定出价或跳过,以避免进一步的成本:
-
这是一个二分类问题,因为模型需要预测出价或不出价。对于此类问题,可以使用多种不同的机器学习算法:
AutoGluon-Tabular、CatBoost、分解机算法、K 最近邻 (k-NN) 算法、LightGBM、线性学习器算法、TabTransformer、XGBoost 算法 -
我们将使用XGBoost 算法 ,当然我们不仅限于SageMaker的内置算法, SageMaker 还允许将自己的 ML 算法作为容器并在 上面运行
-
Amazon SageMaker Training 允许我们创建训练Job,使Job在可扩展的托管基础设施中执行。
-
我们以 parquet 格式存储训练数据。管道模式 可用于 parquet ,因此我们将使用它将数据从 S3 直接流式传输到训练实例。这避免了在训练实例中保存所有数据的必要。
XGBoost训练
我们现在准备使用 EMR 中准备的特征数据来训练一个简单的 XGboost 模型。先定义训练路径和验证集的路径:
training_path = f"{DATA_PREFIX}/train/"
validation_path = f"{DATA_PREFIX}/valid/"
test_path = f"{DATA_PREFIX}/test/"
training_path, validation_path, test_path
# ('processed/sample/train/',
# 'processed/sample/valid/',
# 'processed/sample/test/')
管道模式可用于 parquet 格式,因此我们将使用它将数据从 S3 直接流式传输到训练实例。
我们还通过激活 ShardedByS3Key 选项将训练数据分片到多个实例,以允许使用多个实例训练模型,其中每个实例将接收一部分数据。 对于在多个实例上使用大规模数据进行训练,这是必须的。
from sagemaker.inputs import TrainingInput
s3_input_train = TrainingInput(s3_data='s3://{}/{}'.format(INPUT_BUCKET_NAME, training_path), content_type='application/x-parquet', distribution="ShardedByS3Key", input_mode='Pipe') #
s3_input_validation = TrainingInput(s3_data='s3://{}/{}'.format(INPUT_BUCKET_NAME, validation_path), content_type='application/x-parquet', input_mode='Pipe')
使用SageMaker自带的XGboost 1.2-1版本:
container = sagemaker.image_uris.retrieve('xgboost', boto_session.region_name, '1.2-1')
display(container)
# '246618743249.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/sagemaker-xgboost:1.2-1'
import time
from time import gmtime, strftime
prefix = 'sagemaker/xgb_bid_filtering'
# JOB_TS = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S', time.gmtime())
base_job_name = f'sample-single-cpu-parquet-7-features-training1st'
# 我们将使用按需实例进行训练,但是我们可以使用Spot实例来节省成本,但竞价实例在某些时间可能不可用。
use_spot_instances = False
max_run = 5400 # max 90 mins run
max_wait = 7200 if use_spot_instances else None
# 如果使用spot实例,还需要提供checkpoint路径
checkpoint_s3_uri = (
"s3://{}/{}/checkpoints/{}".format(OUTPUT_BUCKET_NAME, prefix, base_job_name) if use_spot_instances else None
)
print("Checkpoint path:", checkpoint_s3_uri)
output_path='s3://{}/{}/output'.format(OUTPUT_BUCKET_NAME, prefix)
output_path # 's3://aik-sagemaker-emr-sagemakeremrproducttrainingmodel-dzr1jnmdzj7r/sagemaker/xgb_bid_filtering/output'
创建XGBoost模型,并定义超参数:
xgb = sagemaker.estimator.Estimator(container,
role,
# volume_size=150, # default 30GB
base_job_name=base_job_name,
instance_count=1,
instance_type='ml.m5.2xlarge', # Other alternatives for CPU ml.m5.12xlarge. For GPU ml.g4dn.4xlarge, ml.g4dn.xlarge, ml.p3.2xlarge
output_path='s3://{}/{}/output'.format(OUTPUT_BUCKET_NAME, prefix),
sagemaker_session=sagemaker_sess,
enable_sagemaker_metrics=True,
use_spot_instances=use_spot_instances, # used for managed spot training
max_run=max_run, # used for managed spot training
max_wait=max_wait, # used for managed spot training
checkpoint_s3_uri=checkpoint_s3_uri, # used for managed spot training
)
xgb.set_hyperparameters(max_depth=5,
# tree_method='gpu_hist', # Required when GPU instance is chosen
eta=0.2,
gamma=4,
min_child_weight=6,
subsample=0.8,
# silent=0,
objective='binary:logistic',
early_stopping_rounds=20,
num_round=50)
异步启动训练任务:
xgb.fit(inputs={'train': s3_input_train, 'validation': s3_input_validation},
wait=False)
status = sagemaker_sess.describe_training_job(xgb._current_job_name)['TrainingJobStatus']
while(status not in ["Completed", "Failed", "Stopped"]):
time.sleep(30)
status = sagemaker_sess.describe_training_job(xgb._current_job_name)['TrainingJobStatus']
print (status)
此时在SageMaker页面可以看到训练任务正在跑,等待它跑完:

加载训练模型并进行评估
训练工作完成后,让我们在本地加载模型并在测试集上进行评估
TRAINING_JOB_NAME = xgb._current_job_name
TRAINING_JOB_NAME # 'sample-single-cpu-parquet-7-features-tr-2024-02-02-12-59-49-647'
s3_model_path = xgb.model_data
s3_model_path # 's3://aik-sagemaker-emr-sagemakeremrproducttrainingmodel-dzr1jnmdzj7r/sagemaker/xgb_bid_filtering/output/sample-single-cpu-parquet-7-features-tr-2024-02-02-12-59-49-647/output/model.tar.gz'
# 从S3下载模型文件
import os
model_tar_file_local_path = f"./trained_model/{TRAINING_JOB_NAME}/model.tar.gz"
# download trained model locally
if not os.path.exists(os.path.dirname(model_tar_file_local_path)):
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(model_tar_file_local_path))
s3_client.download_file(Bucket=OUTPUT_BUCKET_NAME,
Key=s3_model_path.replace(f"s3://{OUTPUT_BUCKET_NAME}/", ""),
Filename=model_tar_file_local_path)
将模型解压:
import tarfile
# Extract the model tar file and retrieve the model pickle file
with tarfile.open(model_tar_file_local_path, "r:gz") as tar:
tar.extractall(path=f"./trained_model/{TRAINING_JOB_NAME}")
import pickle as pkl
import xgboost as xgblib
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import load_svmlight_file
def model_fn(model_dir):
with open(os.path.join(model_dir, "xgboost-model"), "rb") as f:
booster = pkl.load(f)
return booster
def local_predict(xgb_local, test_libsvm_file):
t_mat = xgblib.DMatrix(test_libsvm_file)
preds = xgb_local.predict(t_mat)
return preds
def local_predict_nparray(xgb_local, np_array):
t_mat = xgblib.DMatrix(np_array)
preds = xgb_local.predict(t_mat)
return preds
下载测试集:
file_type = 'parquet'
# Download test file matching the model
model_folder = f"./trained_model/{TRAINING_JOB_NAME}"
test_file_s3_path = test_files[0]
test_file_local_path = f"./trained_model/{TRAINING_JOB_NAME}/test_set.{file_type}"
s3_client.download_file(INPUT_BUCKET_NAME, test_file_s3_path, test_file_local_path)
xgb_local = model_fn(model_folder)
if file_type == 'parquet':
X_test_pd = pd.read_parquet(test_file_local_path)
X_test = X_test_pd.drop(["label"], axis=1)
X_test.to_numpy().shape
y_test = X_test_pd["label"].to_numpy()
elif file_type == 'libsvm':
X_test, y_test = load_svmlight_file(test_file_local_path, zero_based=True)
在测试集上进行推理:
%%time
if file_type == 'parquet':
local_preds = local_predict_nparray(xgb_local, X_test)
local_y_vals = np.round(local_preds)
elif file_type == 'libsvm':
local_preds = local_predict(xgb_local, test_file_local_path)
local_y_vals = np.round(local_preds)
local_preds, local_y_vals
CPU times: user 18.1 ms, sys: 1.16 ms, total: 19.3 ms
Wall time: 21.8 ms
(array([0.9629985 , 0.00681488, 0.08869029, ..., 0.77757657, 0.77881277,
0.77524304], dtype=float32),
array([1., 0., 0., ..., 1., 1., 1.], dtype=float32))
展示混淆矩阵:
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
def show_confusion_matrix(y_true, y_preds, threshold=0.5):
y_vals = np.where(y_preds > threshold, 1, 0)
cf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_vals)
group_names = ['True Neg','False Pos','False Neg','True Pos']
group_counts = ["{0:0.0f}".format(value) for value in
cf_matrix.flatten()]
labels = [f"{v1}\n{v2}" for v1, v2 in
zip(group_names,group_counts)]
labels = np.asarray(labels).reshape(2,2)
# plt.figure(figsize=(9,7))
ax = sns.heatmap(cf_matrix, annot=labels, fmt='', cmap='Blues')
ax.set_title('Confusion Matrix \n\n');
ax.set_xlabel('\nPredicted Values')
ax.set_ylabel('Actual Values ');
ax.xaxis.set_ticklabels(['No Bid','Bid'])
ax.yaxis.set_ticklabels(['No Bid','Bid'])
plt.show()

计算不同的评估指标来评估模型性能:
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score, matthews_corrcoef
def collect_eval_metrics(true_values, predicted_values, threshold=0.5):
metric_df = pd.DataFrame({"test_roc_auc_score":[round(roc_auc_score(true_values, (predicted_values > threshold)), 5)],
"test_accuracy":[round(accuracy_score(true_values,(predicted_values > threshold)) ,5)],
"test_recall":[round(recall_score(true_values, (predicted_values > threshold)), 5)],
"test_precision":[round(precision_score(true_values, (predicted_values > threshold)),5)],
"test_f1_score":[round(f1_score(true_values, (predicted_values > threshold)),5)],
"test_matthews_corrcoef":[round(matthews_corrcoef(true_values, (predicted_values > threshold)),5)]})
return metric_df
evaluation_metrics_df = collect_eval_metrics(y_test, local_preds)
evaluation_metrics_df

展示概率直方图:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.hist(local_preds)
plt.show()

上图显示了预测概率的分布。我们使用 np.round() 将概率转换为 0 (no_bid) 和 1 (bid) 类。 在这种情况下截止阈值(cut-off threshold)是 0.5,但是对于出价预测用例,false negatives 比 false positives重要得多。 我们可以更改截止阈值以最大限度地减少false negatives.。
更改Cut-off的值
现在,我们将默认截止值 (0.5) 更改为不同的值,并查看对混淆矩阵和评估指标(如精度、召回率等)的影响。
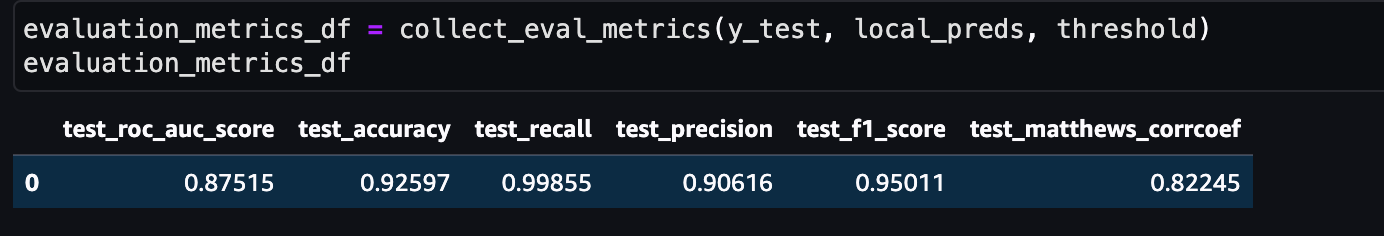
threshold = 0.1

False Neg由原来的44个降低到了7个。其他指标如下:
展示ROC曲线
from sklearn import metrics
def show_roc_curve(y_test, y_preds):
fpr1, tpr1, _ = metrics.roc_curve(y_test, y_preds)
auc_title = plt.title("ROC Curve")
auc_full_model = plt.plot(fpr1, tpr1,
color = 'blue',
label = "full model")
auc_legend = plt.legend(loc = 'lower right')
random_guess = plt.plot([0,1],[0,1],'r--')
xlim = plt.xlim([-0.1,1.1])
ylim = plt.ylim([-0.1,1.1])
ylabel = plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
xlabel = plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.show()
show_roc_curve(y_test, local_preds)

以二进制格式保存模型以便在 ECS 中进行推理
先在本地保存:
xgb_model = xgb_local
xgb_binary_model_path = "xgboost.bin"
xgb_model.save_model(xgb_binary_model_path)
上传到 S3,以便推理应用程序可以在 ECS 中使用它:
binary_model_dir = ssm.get_parameter(Name="/aik/xgboost/path")["Parameter"]["Value"]
binary_model_path = ssm.get_parameter(Name="/aik/xgboost/path")["Parameter"]["Value"]
binary_model_path = binary_model_path.replace("s3://" + bucket + "/", "")
s3_client.upload_file(xgb_binary_model_path, bucket, binary_model_path)
将 Schema 保存为 json,以便在 ECS 中进行推理:
%%writefile schema.json
{
"BidID": "StringType",
"dow": "IntegerType",
"hour": "StringType",
"RegionID": "StringType",
"CityID": "StringType",
"Domain": "StringType",
"AdvertiserID": "StringType",
"BiddingPrice": "LongType",
"PayingPrice": "LongType",
"UserAgent": "StringType"
}
inference_schema= ssm.get_parameter(Name="/aik/pipelineModelArtifactSchemaPath")["Parameter"]["Value"]
inference_schema_path = inference_schema.replace("s3://" + bucket + "/", "")
s3_client.upload_file("schema.json", bucket, inference_schema_path)